Overview

Fallen arches, flat feet, or Plantar fasciitis can cause pain and discomfort in the legs, feet, ankles, Achilles tendon, hips, and low back. In this video, Ron Vaughn, a sports massage therapist, and Christie Powell, a physical therapist, explain how the feet become pronated (fallen arches) and how some simple at-home exercises can strengthen the arch muscles to allevaite pain and discomfort.
Causes
Flat feet can be caused by injury, aging, and weight gain. They can cause pain in the feet and may lead to pain in other parts of the body such as the ankles, knees, or hips. For this reason, it behooves us to treat fallen arches. The question becomes how to do so.
Symptoms
Knee/Hip/Back Pain - When the arch collapses in the foot, it triggers a series of compensations up the joint chain, leading to increased stress on the knee, pelvis and low back. Plantar fasciitis - This condition is characterized by heel pain, especially with the first few steps you take. The plantar fascia stretches as the arch falls, putting stress on the heel. Bunions - If you see a bony bump developing at the base of your big toe, you are likely developing a bunion. It may be swollen, red or painful when it rubs against your shoe. A flattened arch spreads the forefoot and causes the big toe to deviate toward the second toe. Shin splints - This term generally refers to pain anywhere along the shinbone. It is typically due to overuse and is aggravated after exercise and activity.
Diagnosis
Your doctor will ask about your symptoms and medical history. A physical and foot exam will be done. Flat feet can be diagnosed by appearance. To determine if the foot is rigid, you may be asked to do some simple tasks.
What is PES Planovalgus deformity?
Non Surgical Treatment
If you have fallen arches, but you are not experiencing any symptoms, then you probably do not need to seek treatment. If you are experiencing discomfort due to fallen arches, there are several treatment options. These treatment options include elevating the feet and applying ice to ease discomfort and reduce swelling, rest, exercises to stretch the feet, physical therapy, medication, such as anti-inflammatories, steroid injections and orthotic devices or customised arch supportsto wear in the shoes. If you have fallen arches and periodically experience pain related to that condition, it is a good idea to get orthotic devicesor custom arch supports, to wear in your shoes. The other treatment options, like medication and ice, will help to ease pain from fallen arches after you have already begun to experience pain. However, orthotic devices or(custom arch supports)can help to prevent pain from occurring at all. This preventative measure helps many people with fallen arches to avoid pain and prevent worsening of their condition. In severe cases of fallen arches, surgery may be required to correct the problem. You can also help to prevent pain and exacerbation of fallen arches by reducing your risk factors. If you are overweight, try to lose weight. Even a small weight loss can reduce the pressure on your feet significantly. If you are diabetic, manage your blood sugar as best as possible. Losing weight often also improves the condition of diabetics. You should also avoid high-impact activities, like running on the road, tennis, and sports that involve jumping. Try a gentler form of exercise, like swimming, instead. If you have fallen arches, orthotic devices or(custom arch supports)are an important component of your treatment and can help to prevent pain.
Surgical Treatment

This is rare and usually only offered if patients have significant abnormalities in their bones or muscles. Treatments include joint fusion, reshaping the bones in the foot, and occasionally moving around tendons in the foot to help balance out the stresses (called tendon transfer).
After Care
Time off work depends on the type of work as well as the surgical procedures performed. . A patient will be required to be non-weight bearing in a cast or splint and use crutches for four to twelve weeks. Usually a patient can return to work in one to two weeks if they are able to work while seated. If a person's job requires standing and walking, return to work may take several weeks. Complete recovery may take six months to a full year. Complications can occur as with all surgeries, but are minimized by strictly following your surgeon's post-operative instructions. The main complications include infection, bone that is slow to heal or does not heal, progression or reoccurrence of deformity, a stiff foot, and the need for further surgery. Many of the above complications can be avoided by only putting weight on the operative foot when allowed by your surgeon.

Fallen arches, flat feet, or Plantar fasciitis can cause pain and discomfort in the legs, feet, ankles, Achilles tendon, hips, and low back. In this video, Ron Vaughn, a sports massage therapist, and Christie Powell, a physical therapist, explain how the feet become pronated (fallen arches) and how some simple at-home exercises can strengthen the arch muscles to allevaite pain and discomfort.
Causes
Flat feet can be caused by injury, aging, and weight gain. They can cause pain in the feet and may lead to pain in other parts of the body such as the ankles, knees, or hips. For this reason, it behooves us to treat fallen arches. The question becomes how to do so.
Symptoms
Knee/Hip/Back Pain - When the arch collapses in the foot, it triggers a series of compensations up the joint chain, leading to increased stress on the knee, pelvis and low back. Plantar fasciitis - This condition is characterized by heel pain, especially with the first few steps you take. The plantar fascia stretches as the arch falls, putting stress on the heel. Bunions - If you see a bony bump developing at the base of your big toe, you are likely developing a bunion. It may be swollen, red or painful when it rubs against your shoe. A flattened arch spreads the forefoot and causes the big toe to deviate toward the second toe. Shin splints - This term generally refers to pain anywhere along the shinbone. It is typically due to overuse and is aggravated after exercise and activity.
Diagnosis
Your doctor will ask about your symptoms and medical history. A physical and foot exam will be done. Flat feet can be diagnosed by appearance. To determine if the foot is rigid, you may be asked to do some simple tasks.
What is PES Planovalgus deformity?
Non Surgical Treatment
If you have fallen arches, but you are not experiencing any symptoms, then you probably do not need to seek treatment. If you are experiencing discomfort due to fallen arches, there are several treatment options. These treatment options include elevating the feet and applying ice to ease discomfort and reduce swelling, rest, exercises to stretch the feet, physical therapy, medication, such as anti-inflammatories, steroid injections and orthotic devices or customised arch supportsto wear in the shoes. If you have fallen arches and periodically experience pain related to that condition, it is a good idea to get orthotic devicesor custom arch supports, to wear in your shoes. The other treatment options, like medication and ice, will help to ease pain from fallen arches after you have already begun to experience pain. However, orthotic devices or(custom arch supports)can help to prevent pain from occurring at all. This preventative measure helps many people with fallen arches to avoid pain and prevent worsening of their condition. In severe cases of fallen arches, surgery may be required to correct the problem. You can also help to prevent pain and exacerbation of fallen arches by reducing your risk factors. If you are overweight, try to lose weight. Even a small weight loss can reduce the pressure on your feet significantly. If you are diabetic, manage your blood sugar as best as possible. Losing weight often also improves the condition of diabetics. You should also avoid high-impact activities, like running on the road, tennis, and sports that involve jumping. Try a gentler form of exercise, like swimming, instead. If you have fallen arches, orthotic devices or(custom arch supports)are an important component of your treatment and can help to prevent pain.
Surgical Treatment

This is rare and usually only offered if patients have significant abnormalities in their bones or muscles. Treatments include joint fusion, reshaping the bones in the foot, and occasionally moving around tendons in the foot to help balance out the stresses (called tendon transfer).
After Care
Time off work depends on the type of work as well as the surgical procedures performed. . A patient will be required to be non-weight bearing in a cast or splint and use crutches for four to twelve weeks. Usually a patient can return to work in one to two weeks if they are able to work while seated. If a person's job requires standing and walking, return to work may take several weeks. Complete recovery may take six months to a full year. Complications can occur as with all surgeries, but are minimized by strictly following your surgeon's post-operative instructions. The main complications include infection, bone that is slow to heal or does not heal, progression or reoccurrence of deformity, a stiff foot, and the need for further surgery. Many of the above complications can be avoided by only putting weight on the operative foot when allowed by your surgeon.









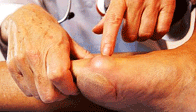
 A bunion is the enlargement of the joint at the base of the big toe. It occurs as a result of the misalignment of the bones of the big toe. This leads to stretching of the ligaments and tendons around the big toe joint and causes soft tissue over the joint to become inflamed and painful. There may be additional bone formation (exostosis) in the joint and the skin around the joint may become red and tender. Over time the cartilage in the joint can break down, leading to arthritis.
A bunion is the enlargement of the joint at the base of the big toe. It occurs as a result of the misalignment of the bones of the big toe. This leads to stretching of the ligaments and tendons around the big toe joint and causes soft tissue over the joint to become inflamed and painful. There may be additional bone formation (exostosis) in the joint and the skin around the joint may become red and tender. Over time the cartilage in the joint can break down, leading to arthritis.